
2002 International Telecommunications Symposium
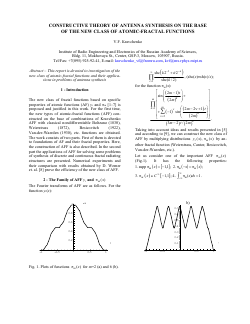
Constructive Theory of Antenna Synthesis on the Base of the New Class of Atomic-Fractal Functions
V.F. Kravchenko
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.63
Keywords:
Abstract
"This report is devoted to investigation of the new class of atomic-fractal functions and their applications in problems of antenna synthesis."Download
An Array of E-shaped Probe-Fed Microstrip Elements for Wireless Communications
Marcos V. T. Heckler, Eduardo S. Neves, Ricardo Schildberg, J. C. da S. Lacava
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.66
Keywords:
Abstract
"This paper discusses a new microstrip antenna array for wireless communication. Initially, the basic array element, an E-shaped probe-fed patch, is analyzed by comparisons between numerical and measured results. After that, a two-element subarray is discussed. Simulated results, obtained by using Ensemble 8.0™ and IE3D™ packages, and experimental ones are presented. Good agreement between these results is obtained. Finally, a sixelement array is designed and analyzed by numerical computations."Download

Analysis of Antenna Arrays Configurations with Random Parameters
Wamberto J. L. Queiroz, Marcelo S. Alencar, Fabricio G. S. Silva
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.72
Keywords: Array antennas random coefficients random spacing array factor
Abstract
"This paper presents a performance analysis of two linear arrays structures considering the effect of excitation coefficients and random separation between elements. The results obtained show that these configurations can produce good radiation patterns in terms of side lobes level and directivity. Depending on the chosen parameters the irradiation pattern can be optimized as compared to the one obtained using binomial coefficients and as good as the patterns obtained using Dolph-Tschebyscheff. This method can be used in order to get a smoother irradiation pattern and can be useful to control de irradiation pattern in response to user mobility. Another advantage is related to the numerical processing involved in the computation of excitation coefficients. They are chosen randomly from a convenient set, while in other cases they are computed in real time and depend on antenna dimensions, a task which can be computer intensive."Download

Intelligent System to Cancel Multiple Interferences
Osmar de Araújo Dourado Júnior, Adrião D. Dória Neto, Wilson da Mata
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.76
Keywords:
Abstract
"This paper presents an intelligent system for interference signals cancelling in a linear antennas array. The method combines Blind Source Separation a modular structure formed by radial basis functions neural networks− MRBF that estimates the AOA− Angle of Arrival of the multiple independent incident signals on the sensors array and supplies these informations to the GSC–Generalised Sidelobe Canceller, that through an adaptive way cancels the interference signals, mantaining the desired signal. "Download

25 GHz Monolithic Oscillator with Frequency Divider in SiGe Bipolar Technology
Günter Ritzberger, Josef Böck
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.80
Keywords:
Abstract
"This paper presents a monolithic voltage-controlled oscillator with static frequency divider in a pre-production 0.4 \u00b5m SiGe bipolar technology for broadband communication applications. The voltage-controlled oscillator operates from 17.8 GHz to 25 GHz. The division ratio of the static frequency divider is 16. The circuit consumes 500 mW from the 5 V supply including the two output bu\ufb00ers."Download
A CMOS RF front-end Switch Topology
Robson N. de Lima, Bernard Huyart
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.84
Keywords:
Abstract
"This paper describes a CMOS RF Single Pole Double Through (SPDT) switch used in the front-end of a transceiver. Its topology is based on the association of an active quasi-circulator and an RF Single Pole Single Through (SPST) Switch."Download

Far Field, Near Field and SAR Simulation for Cell Phones Operating Close to the Head
Mateus Bonadiman, Claudio R. Fernández, Álvaro A. de Salles
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.88
Keywords: Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) Cellular Phone Biological Effects Planar Antennas
Abstract
"The Finite-Difference Time-Domain (FDTD) method to calculate the cellular phone far and near field and the specific absorption rate (SAR) in the user\u2019s head is described. The conventional \u03bb/4 monopole and a simple planar antenna are simulated. A multidimensional grid is developed to optimize simulations in the near and in the far field, in the presence and in the absence of the cellular phone user\u2019s head at 1.9 GHz. These calculations show that significant improvement in the antenna radiation efficiency and in the reduction of the SAR in the head are 1 obtained when planar antennas are used."Download

A Genetic Algorithm for the Determination of Multiple Angles of Arrival in Linear Arrays of Antennas
Bruno Galindo de Góes, Adrião Duarte Dória Neto, Wilson da Mata
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.94
Keywords: Genetic algorithms angle of arrival adaptive antennas
Abstract
"This work deals with the study of genetic algorithms in the determination of the directions of arrival of incident signals in linear arrays of antennas. For such, techniques of spectral esteem are used to define a spectral density function. To leave of this function the development of genetic algorithms becomes possible that will go to determine the values for which the function is maximized. Such values are the angles that indicate the directions of the incident signals."Download
A Pseudo Inverse Solution Method Applied to an Adaptive Antenna
Fábio A. L. Gomes, Adrião Duarte D. Neto, Aldayr D. Araújo, Wilson da Mata
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.100
Keywords: Adaptive Filters Adaptive Antenna Pseudo Inverse Matrix
Abstract
"The adaptive antenna theory has been studied in several application fields such as radar, sonar, mobile communications, geophysics exploitation, etc. In all these cases, the different methods used to solve problems in the adaptive antenna approach generally use the same procedure, which is related to the increasing of the directivity of the antenna array and to the interfering signals adaptive cancellation. The research to obtain more efficient methods has motivated the adaptive antennas approach to use traditional Least Mean Square (LMS) method or state space variables methods such as Kalman Filter and State Observers. This work presents an algorithm to obtain the optimum gains of the Generalized Side Lobe Canceller Filter (GSC Filter) using a pseudo inverse matrix. Additionally, the importance of the regularization factor to the robustness of the method is verified. The method is recursive, with low computational complexity and fast calculation of the optimum gains. The method is applied to the cancellation of interfering signals in a non-stationary condition of an adaptive antenna array. A matrix regularization process is developed to get a robust method and a better matrix conditioning. The simulation results show the efficiency of the proposed method to cancel interfering signals in planar antennas. The simulation results were done with a 3x3 half wavelength elements in planar array for both signals (desired and interfering). A 40dB was considered for the relationship between the desired signal and the interfering signal. The irradiation diagrams were obtained in two dimensions for a fixed angular coordinate. The method seems to be efficient to generate null signals in the interfering signal direction. The LMS method was used to compare the performance with the proposed method. "Download

A Static 4:1 Frequency Divider up to 16 GHz in 120 nm CMOS
Hans-Dieter Wohlmuth, Daniel Kehrer, Werner Simbürger
DOI: 10.14209/its.2002.106
Keywords:
Abstract
"A completely integrated 16 GHz static 4:1 frequency divider in 120 nm CMOS is presented. The divider operates up to 16 GHz and features an enhanced input sensitivity of 0 dBm over a broad input band of 14 GHz. The circuit draws 60 mA from a single 1.5 V supply. To drive 50 \u03a9 loads up to 4 GHz, an output buffer is also included in the divider circuit."Download